If You Eat Meat and Dairy What Are Your Chances of Getting Cancer Again
Foods from animal sources
Animal foods is a term used to describe all foods of animate being origin. These foods may be derived from the animate being flesh itself (for case, meat, fish and poultry) or foods that are produced past animals (for example, eggs, every bit well as dairy products such as milk and products fabricated from milk including cheese, butter, ghee and yoghurt)
Animal foods are generally a skillful source of protein, but the fat content varies co-ordinate to the specific species from which they are derived. Dairy products are a good source of calcium. Consumption of foods such as red meat and fish mostly increases with economical development, whereas consumption of dairy products is variable, particularly in Asia where many populations are lactose intolerant.
Animal foods such as meat and fish may exist processed before consumption by smoking, curing, salting or past adding preservatives. Meat and fish are likewise often cooked using very high temperatures during frying, grilling (broiling) or barbecuing (charbroiling). These methods of processing and grooming may touch on the chemic composition as well as the nutritional value of animate being foods.
OUR MAJOR FINDINGS ON CANCER AND Brute FOODS
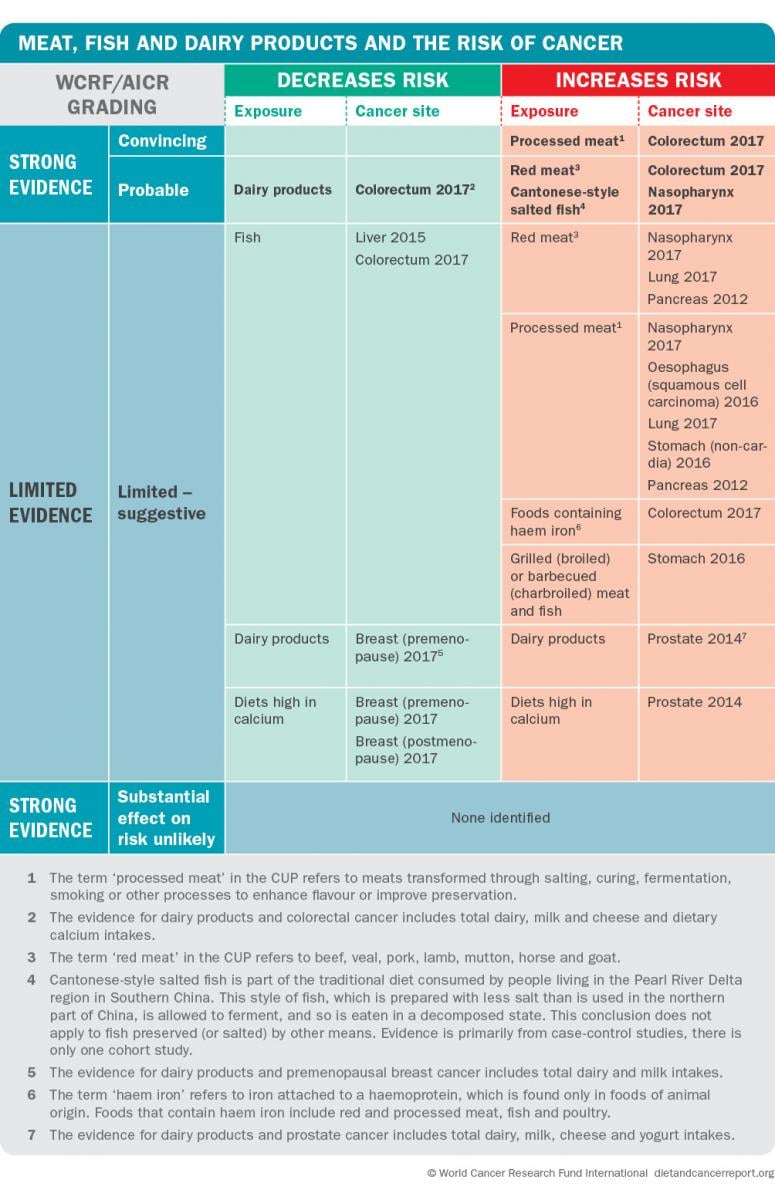
There is potent evidence that consuming:
- red meat INCREASES the chance of colorectal cancer
- processed meat INCREASES the run a risk of colorectal cancer
- Cantonese-style salted fish INCREASES the run a risk of nasopharyngeal cancer
- dairy products DECREASE the run a risk of colorectal cancer
> See more graphics in our toolkit
For people who eat meat, swallow no more than than moderate amounts of red meat, such as beefiness, pork and lamb, and eat petty, if any, candy meat
– This is the stance of the Practiced Panel and forms the basis of our Recommendation on red and processed meat
For ruby meat, processed meat and Cantonese-mode salted fish the bear witness shows that, in full general, the more than people consume, the higher the take a chance of some cancers. In contrast, the show shows that, in general, the more dairy products people consume, the lower the take a chance of colorectal cancer.
A global recommendation about consumption of Cantonese-way salted fish has not been made as this type of fish is consumed only in specific parts of the world. Nonetheless, the Panel advises that Cantonese-mode salted fish should not exist consumed.
The Panel did not base of operations a recommendation on the strong prove that the consumption of dairy products decreases the take a chance of colorectal cancer as in that location is some other evidence that is suggestive of an increased risk of prostate cancer, although that evidence fell below the full general threshold required for making a recommendation. For more data on when the prove is divergent between cancer sites, download the chapter of the Third Expert Report on Recommendations.
Mechanisms
This section covers the master hypotheses and is not based on a systematic or exhaustive search of the literature.
Ruddy meat and cancer
Cooking meats at loftier temperatures, prolonged exposure to rut and cooking by various types of grilling results in the formation of heterocyclic amines and polycyclic effluvious hydrocarbons both of which have been linked to colorectal cancer development in experimental studies.
In addition, haem iron, which is nowadays at loftier levels in scarlet meat, has been shown to promote colorectal tumorigenesis by stimulating the endogenous germination of carcinogenic N-nitroso compound.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which are formed when organic substances like meat are burnt incompletely, may as well have carcinogenic potential. Grilling (broiling) and barbecuing (charbroiling) meat, fish, or other foods with intense heat over a straight flame results in fat dropping on the hot burn, causing flames; these flames contain polycyclic effluvious hydrocarbons that stick to the surface of food.
Candy meat and cancer
Overall it is likely that a combination of mechanisms contribute to higher chance of colorectal cancer amongst people consuming high quantities of processed meat. Like to red meat, processed meat is rich in fatty, protein and haem fe which can promote tumorigenesis through the mechanisms described higher up.
Processed meats are often cooked at high temperatures which tin lead to increased exposure to heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Processed meat is invariably higher in fat content than red meat which may promote carcinogenesis through synthesis of secondary bile acids; however, homo data supporting this hypothesis are weak.
Processed meat is too a source of exogenously derived Due north-nitroso compounds, which may have carcinogenic potential.
Dairy and cancer
Observed changed associations between intake of dairy products and colorectal cancer development have been largely attributed to their loftier calcium content. In addition to calcium, lactic acid-producing leaner may also protect against colorectal cancer,
while the casein and lactose in milk may increase calcium bioavailability. Other nutrients or bioactive constituents in dairy products, such as lactoferrin, vitamin D (from fortified dairy products) or the short-chain fatty acid butyrate may also impart some protective functions against colorectal cancer, only these require much better elucidation.
The CUP Panel ended that the evidence was generally consistent for dairy products, milk, cheese and dietary calcium, and showed a decreased chance of colorectal cancer with higher consumption.
> Read more than about the cancer process
Source: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/meat-fish-and-dairy/
0 Response to "If You Eat Meat and Dairy What Are Your Chances of Getting Cancer Again"
Post a Comment